17. Deck of Cards
Sunhyup Lee. (2024). To be a successful candidate for the coding test. goldenrabbit. p.215.
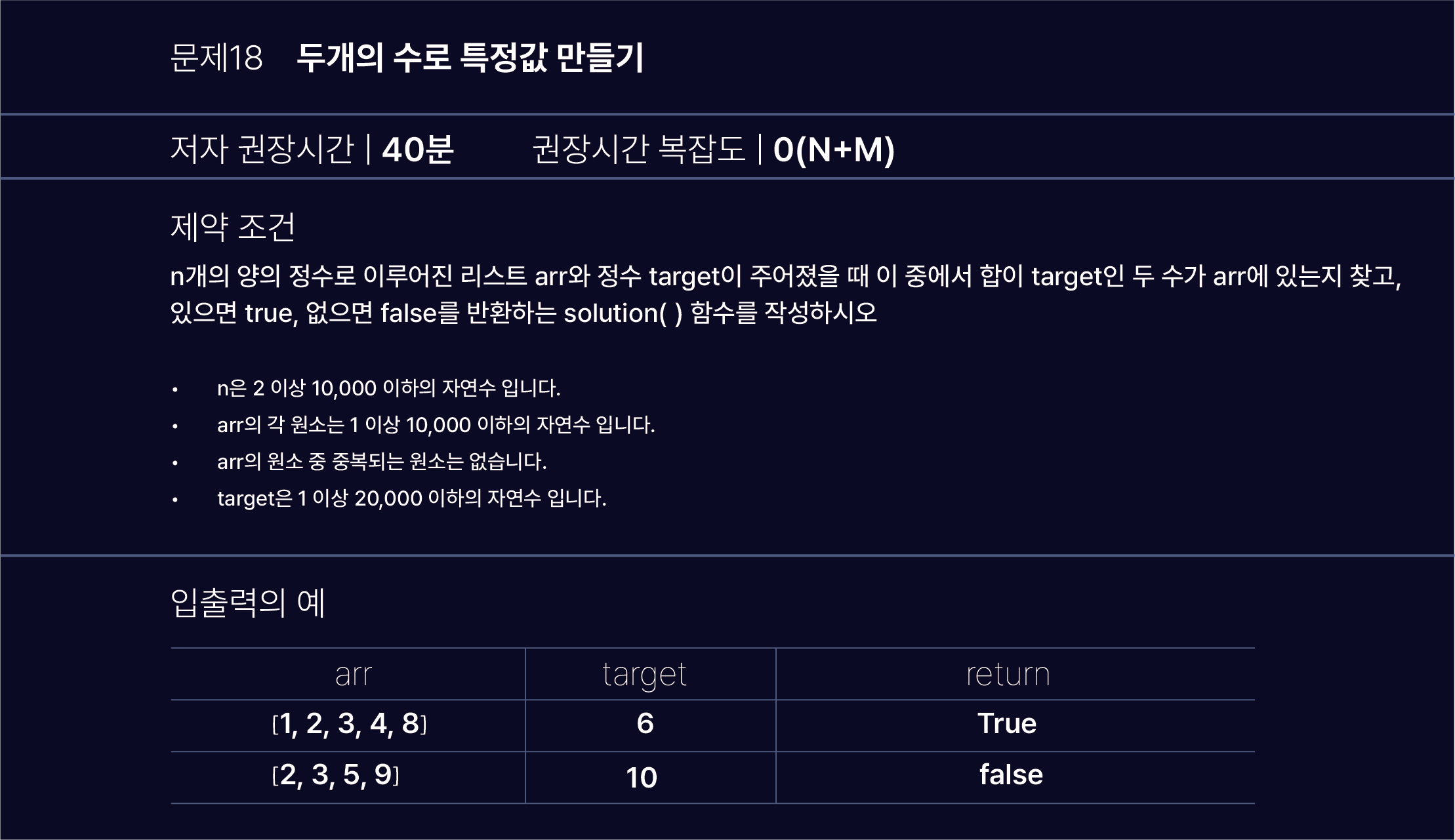
Problem solving
1. Hash를 이용하여 풀기
(1) target에서 num을 뺐을 경우, 동일한 num이 나와서는 안됨 (동일 숫자 안됨)
(2) target에서 num을 뺐을 경우, 0보다 크거나 같아야 함 (어떤 num이든 target보다 커서는 안됨)
(3) hashtable에서 해당 값이 존재 해야함 (해당 num이 테이블 내 존재)
function countSort(arr, k) {
const hashtable = new Array(k + 1).fill(0);
for (const num of arr) {
if (num <= k) {
hashtable[num]++;
}
}
return hashtable;
}
function solution(arr, target) {
const hashtable = countSort(arr, target);
for (const num of arr) {
const complement = target - num;
if (
complement !== num &&
// `target`에서` num`을 뺐을 경우, 동일한 `num`이 나와서는 안됨 (동일 숫자 안됨)
complement >= 0 &&
// `target`에서` num`을 뺐을 경우, 0보다 크거나 같아야 함 (어떤 num이든 target보다 커서는 안됨)
hashtable[complement] > 0
// hashtable에서 해당 값이 존재 해야함 (해당 num이 테이블 내 존재)
) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
console.log(solution([1, 2, 3, 4, 8], 6)); // true
console.log(solution([2, 3, 5, 9], 10)); // false
2. HashMap 활용하여 풀기
🧐Q. arr의 값이 커질경우, 배열이 너무 커지는 문제는 어떻게 해결할 수 있을까?
function solution(arr, target) {
const hashmap = new Map();
// 해시맵에 배열의 값과 빈도를 저장
for (const num of arr) {
hashmap.set(num, (hashmap.get(num) || 0) + 1);
}
// 타겟 값을 만족하는 쌍이 있는지 확인
for (const num of arr) {
const complement = target - num;
// 타겟 값을 만족하는 쌍이 있는 경우
if (hashmap.has(complement)) {
// 자기 자신과 짝이 되는 경우를 처리할 필요 없음
if (complement !== num || hashmap.get(num) > 1) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
console.log(solution([1, 2, 3, 4, 8], 6)); // true
console.log(solution([2, 3, 5, 9], 10)); // false
개선된 방식의 장점
- 공간 효율성:
- 해시맵을 사용하므로 배열 크기와 상관없이 실제로 등장하는 숫자만 저장.
- 공간 복잡도:
O(n)(배열 크기n에 비례).
- 시간 효율성:
- 숫자를 해시맵에 저장:
O(n)(한 번 순회). - 숫자의 존재 여부 확인:
O(1)(평균적으로 해시맵의 조회는 상수 시간). - 시간 복잡도: 전체적으로
O(n).
- 숫자를 해시맵에 저장:
예제) 입력: [1, 2, 3, 4, 8], target = 6
1. 해시맵 생성:
hashmap = { 1: 1, 2: 1, 3: 1, 4: 1, 8: 1 };
2. 첫 번째 숫자 num = 1일 때:
complement = 6 - 1 = 5.hashmap에5가 없음. 다음 숫자로 진행.
3. 두 번째 숫자 num = 2일 때:
complement = 6 - 2 = 4.hashmap에4있음.true반환.